ISO 14001:2015
Introduction To The Standard
The International Standard ISO 14001:2015 defines criteria for an Environmental Management System (EMS); which if implemented and maintained effectively, can provide an organization with reassurance that environmental risk is being managed and improved.
ISO 14001 is applicable to any organization regardless of size, sector, or geographical location. Whilst the Standard sets out a framework for environmental management, it has been devised to give the flexibility to apply to all companies and organizations.
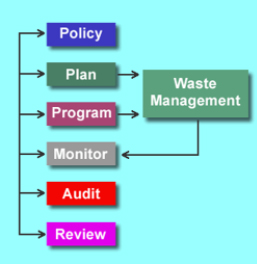
ISO 14001 requires effective demonstration that a systematic approach has been taken to prevent pollution and to have processes in order to manage environmental risk. Once a policy framework has been put into place along with processes to facilitate the organizations’ commitment, the Standard then asks an organization to audit, review, and improve the system to affirm that a commitment to continuous improvement is being achieved.
The Standard fundamentally comes in two parts; “The Standard” and then “Annexes” which provide help and explanation.
Environmental Management System
A Management Tool With Practical Benefits
An environmental management system (EMS) conforming to the international standard, ISO14001, provides the structural framework for an organization to deal with its environmental issues. Some advantages of incorporating environmental management into existing business practice are:
- proactive environmental responsibility,
- meeting the due diligence required of directors and managers,
- financial savings,
- a sustainable competitive advantage.
- An effective integrated management system incorporates EMS, occupational health and safety (OH&S), and quality management.
Benefits Of Implementation
All “management ISO’s” have a similar fundamental benefit. They provide a framework of action that; if implemented appropriately, provides internal control. In the case of ISO 14001, the execution of the standard provides a control for an organization’s activities, products, or services and the interaction with the environment. This, in turn, can increase the long-term viability of the organization and where appropriate a higher regard for its asset value.
Whilst there are other numerous benefits to achieving ISO 14001 (and some will be more appropriate depending upon what sector an organization operates) the following benefits are likely in most cases:
1- Demonstration of Leadership
By testing environmental controls against the internationally recognized environmental Standard, an organization demonstrates ethical environmental leadership to its Stakeholders which includes customers, employees, and Regulators. The achievement of 14001 also provides assurance to a Board of Directors, Trustees, or owners that there is management control regarding environmental risks inherent within an organization.
2- Economic benefit
In a global marketplace where all sectors have to compete in some form or other, demonstration of ethical environmental leadership through “good environmental stewardship”, can be the deciding factor for being selected to supply the goods or services that an organization provides. Having ISO 14001 also may give a Unique Selling Point (USP) that increasingly provides one of the fundamentals when promoting an organization. A fundamental part of the Standard is conformance to appropriate environmental regulatory requirements or other obligations that are deemed as important as a regulatory requirement. A system that checks on.
adherence to legislation mitigates the risk of environmental liability prosecution. Whilst this is not a direct saving to an organization, the outcome of unregulated activities that deleteriously affect the environment will result in ever-increasing fines.
Most organizations or businesses consume resources of one form or another. Whilst the Standard doesn’t direct an organization to measure something specifically, examining the resources that are consumed, for example, energy
3- Internal audit and Management Review
ISO 14001 provides the framework to check what controls have been put into place through the use of internal audit and provides a way in which to monitor and improve. A Management Review process then allows Top Management to take a “step back” and determine how well the system is working within the context of the organization and whether it requires modification to meet future changes in a process, resources, or regulatory framework. Internal audits and Management Reviews when combined with an audit from a certification body, such as NQA, provide assurance that the EMS is meeting the requirements of the organization and the ISO 14001 Standard.
PDCA Cycle
Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) is an iterative, four-stage approach for achieving continual improvement. It involves systematically testing possible solutions, assessing the results, and implementing the ones that are shown to work.
At the “heart” of this approach is leadership. The importance of leadership at all levels, but particularly by Top Management, cannot be underestimated to operate an EMS successfully, to achieve performance levels required, and generate continual improvement.
In the context of an EMS, PDCA is translated into the following:
Plan:
Understand the context of the organization, establish environmental objectives and processes necessary to deliver results
in accordance with the organization’s environmental policy, understand risk and opportunities and determine the support required to achieve the outcomes required.
Do:
Implement the processes as planned to include operational planning and control and emergency preparedness and response.
Check:
Monitor, measure, and evaluate environmental performance to include internal audit and Management Review.
Act:
Take actions to continually improve to include addressing nonconformity.