ISO 9001: 2015
Is Your Organization Concerned?
- Superior Quality
- Risk-based thinking
- Customer Satisfaction
- Better Market Image
- Productivity & efficiency Improvement
- conformance to international standards
- International acceptance
- Topline growth & bottom-line improvement

ISO 9001 requirements are generic and intended to be applicable to any type of organization
How Can “Aisc Group” Help?
Our Team offers a variety of Consulting Services and Solutions.
We understand that each organization or person is unique. Our Solutions are comprehensive and will be customized to meet your specific needs.
- Provides a well-planned and stage-by-stage audit program.
- A sound, coherent and non-disruptive assessment.
- We have an enviable record of customer satisfaction.
ISO 9001 Quality Management Principles
The ISO 9001 series of standards-based is on eight dynamic Quality Management System Principles. These Principles are:-
- Customer Focus
- Leadership
- Engagement of People
- Process Approach
- Continual improvement
- Evidence-based decision making
- Relationship management
ISO 9001, the requirement standard, includes the following main sections:
- Quality Management System
- Management Responsibility
- Resource Management
- Product Realization
- Measurement Analysis and Improvement
How Do Businesses Benefit from ISO 9001: Certification?
Your organization, whatever your business lines are, realizes a handful of benefits through certification against ISO 9001:2015 Standards, which confers upon your business an infinite vista for returns. Such benefits can be categorized as follows.
Internal Benefits: -
- Better management of core business processes.
- Increased awareness of quality among staff.
- Improved productivity and quality.
- Improved internal communications.
- Reduced wastage and cost per unit/service through
- improved product reliability
- better process control and flow of internal processes and improving process design
- improved consistency of service and product performance
- optimal use of resources and time
- reduction in product scrap, rework, and rejection
External Benefits: -
- Competitive Advantage and increased marketing and sales opportunities through access to new markets.
- Improves Customer Demand.
- Protect Your Business.
- Easy & Cost-Effective.
- Qualify for Contracts.
- Increased Credibility.
- Enhancing higher customer satisfaction levels.
- Better meeting the continuously increasing customer needs and minimizing risks inherent in unmet customer expectations.
Compliance to 9001:2015 required by customers in their tendering and purchase specificationPlacing the business on the competitive edge through consistent quality products providing greater confidence on the part of customers
Describing and documenting the business’s commitment to quality, as well as to its policies and procedures
Involving and motivating the management and staff leads to higher performance levels as well as improved staff communication, morale, and job satisfaction
Through its worldwide acceptance and use, the 9001:2015 Standards provide an effective means for improving the performance of individual organizations and provide confidence to people and organizations that products, goods, and services will meet their expectations, thereby enhancing trade, global prosperity, and individual well-being
What is ISO 9001 standard/certification?
ISO 9001:2015 is an international standard that gives requirements for an organization’s Quality Management System (“QMS”). It is part of a family of standards published by the International Organization for Standardization (“ISO”) often referred to collectively as the “ISO 9000 series”. For this reason, you may sometimes hear your suppliers refer to being “ISO 9000 certified”, or having an “ISO 9000-compliant QMS”.
This will normally mean that they are claiming to have a QMS meeting the requirements of ISO 9001:2015, the only standard in the ISO 9000 family that can be used for the purpose of conformity assessment. It is important to understand however, that ISO is the body that develops and publishes the standard – ISO does not “certify” organizations, certification done by various certification bodies against ISO 9001 QMS standard published by ISO.
The objective of ISO 9001:2015 is to provide a set of requirements that, if they are effectively implemented, will provide you with confidence that your supplier can consistently provide goods and services that:
- Meet your needs and expectations and – comply with applicable regulations
- It covers a wide range of topics, including your supplier’s top management commitment to quality, its customer focus, adequacy of its resources, employee competence, process management (for production, service delivery, and relevant administrative and support processes),
- Quality planning, product design, review of incoming orders, purchasing, monitoring and measurement of its processes and products, calibration of measuring equipment, processes to resolve customer complaints, corrective/preventive actions, and a requirement to drive continual improvement of the QMS.
- Finally, yet importantly, there is a requirement for your supplier to monitor customer perceptions about the quality of the goods and services it provides.
ISO 9001 is an international quality certification that defines minimum requirements for a company’s Quality Management System (QMS). A company’s QMS comprises the organization’s policies, procedures, and other internal requirements that ensure customer requirements are met with consistency resulting in customer satisfaction.
Some of the areas of the company within the scope of ISO 9001 include:
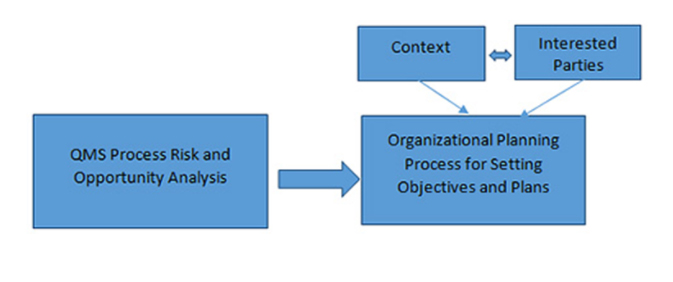
- Context of the organization
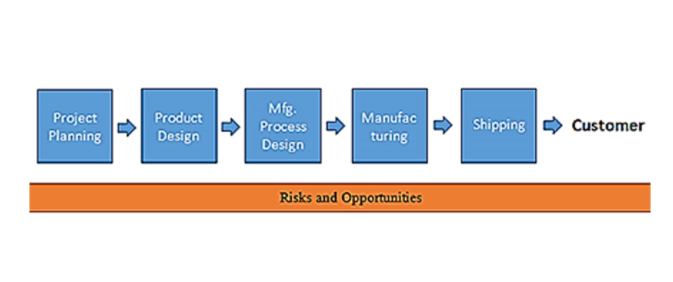
- Risk-based thinking
- Customer contracts
- Hiring and employee training
- Design and development of products and services
- Production and delivery of products and services
- Selection and managing of suppliers
- Management responsibility
- Internal quality audits
- Monitoring and measuring
- Continual improvement
- Corrective and preventive action-
To receive an ISO 9001 certification a company must put the required QMS processes and controls in place, monitor the performance of its processes, and demonstrate continual improvement. Most companies hire an experienced consulting firm to assist with these preparations. Once the QMS is in place, a registrar (or certification body) is hired to audit the company’s compliance with ISO 9001 requirements. If discrepancies are found during the audit, they must be corrected before the ISO 9001 certificate is issued. The ISO 9001 certification must be maintained through regular audits (bi-annual or annual) conducted by the selected registrar.